Species
Mouse
Fields of application
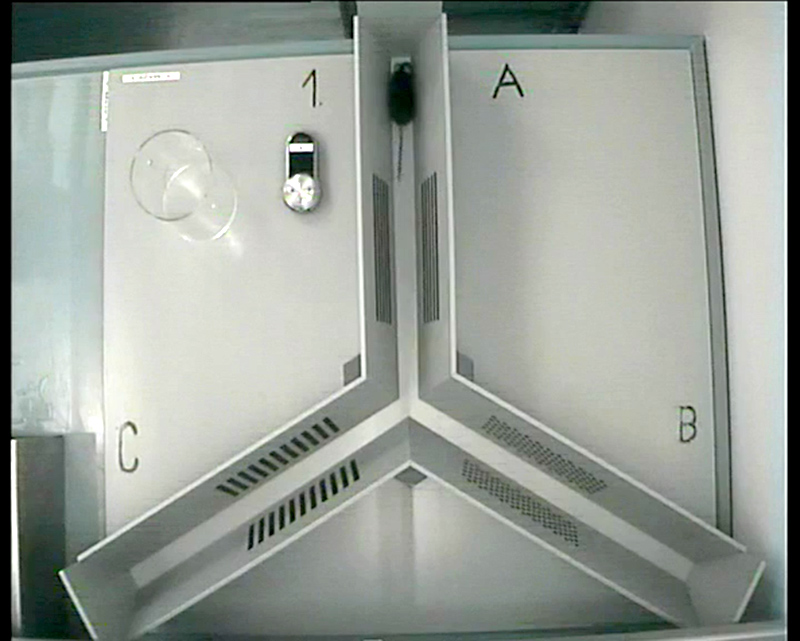
Spontaneous alternation rates (SAP) in the Y-Maze can be used as a simple and rapid procedure to assess spatial learning in rodents. Alternations are defined as successive entries into the three arms of a triangular Y-shaped maze in overlapping triplet sets.
The model can be used for the following fields of application:
- Central nervous system damage
- Disease effects on spatial learning
- Drug administration
- Therapeutic efficacy
- Proof of concept
Endpoints / outcome parameter
- Spontaneous alteration behaviour
Readout parameter
- Time spend it arms [sec]
- Distance [cm]
- Arm entries [counts]
- SAP [%]
Quality management and validation
- Controls
- Randomisation
- Blinded data collection and analysis
- Biometric expertise
- Internal quality management