Inflammatory bowel diseases (IBD), including Crohn’s disease and ulcerative colitis, are chronic-relapsing disorders of the gastrointestinal tract with multifactorial pathogenesis. The model of dextran sulfate sodium (DSS)-induced colitis is a widely used animal model in basic and translational IBD research. We have developed a refined and more translational relevant chronic DSS-induced colitis model that is primarily used for testing the efficacy of potential therapeutics. To account for the shift in the gut microbiota observed in IBD patients, we further developed a bacteria-induced model that better reflects the natural etiology of IBD. Both models are applicable to the evaluation of new therapies and the analysis of IBD pathogenesis.
Mouse models for inflammatory bowel disease (GLP-like / GLP)
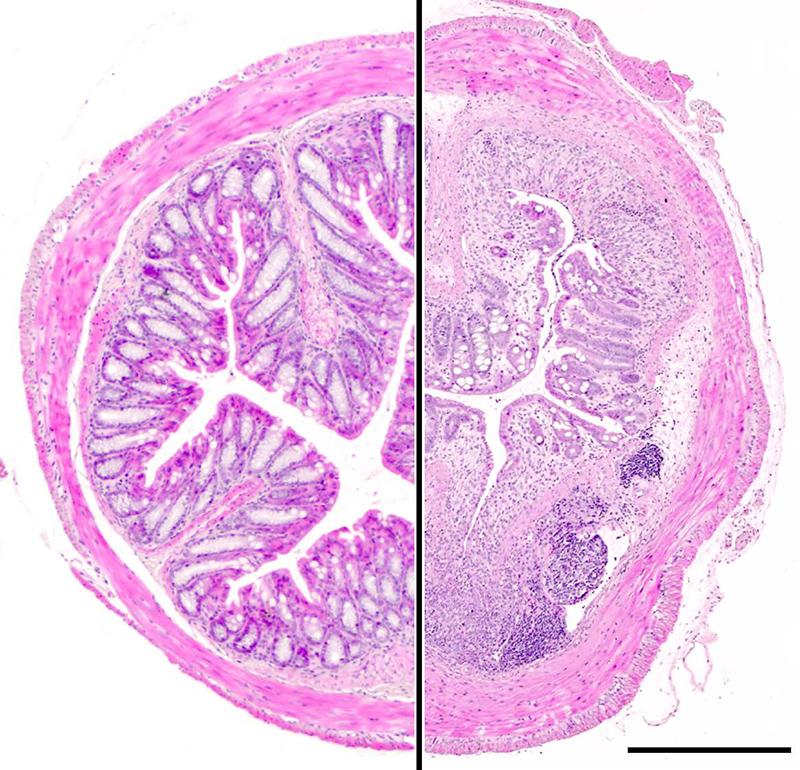
Tissue architecture of the distal colon in a healthy animal (left) and in chronic DSS-induced colitis (right). Scale bar: 500 µm
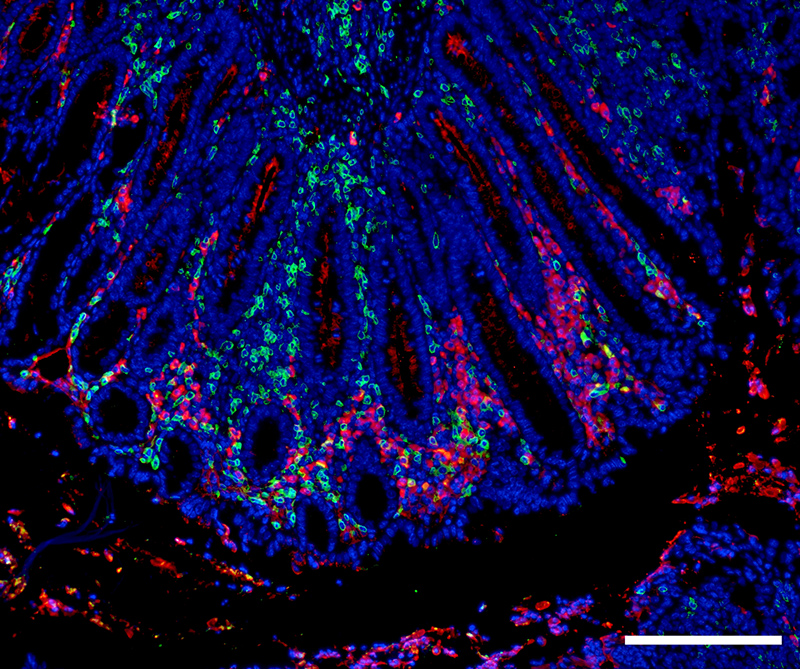
Expression of Immunoglobulin A (red) and T helper cells (CD4; green) in the distal colon of an animal with chronic DSS-induced colitis. Scale bar: 100 µm
Species
Mouse
Fields of application
- Diagnosis and therapy models for IBD
- Testing of potential therapeutics for IBD
- Evaluation of application/treatment protocols for therapeutic agents
- Efficacy and safety studies for drug approval (GLP-like and GLP)
Endpoints / outcome parameters
- Clinical score
- Imaging / monitoring of gut wall lesions
- Gut permeability
- Histopathological score / colon length
- Profile of immune cells / inflammatory markers (e.g. cytokines) in colon tissue
- Profile of microbiota composition
- Expression of disease-relevant tissue markers (e.g. tight junction proteins)
Readout parameters
- Daily evaluation of clinical parameters
- Small animal endoscopy
- FITC-Dextran test
- Histology
- Immunohistochemistry / immunofluorescence
- Flow cytometric analysis / cell sorting
- ELISA / multiplex analysis
- Quantitative real-time PCR
- 16S rRNA sequencing
Quality management and validation
- Internal quality management (certified GLP test facility)
- Use of reference compounds (standard-of-care therapies)
- Randomisation
- Blinded induction / data acquisition and analysis
- Biometric expertise