Species
Mouse
Fields of application
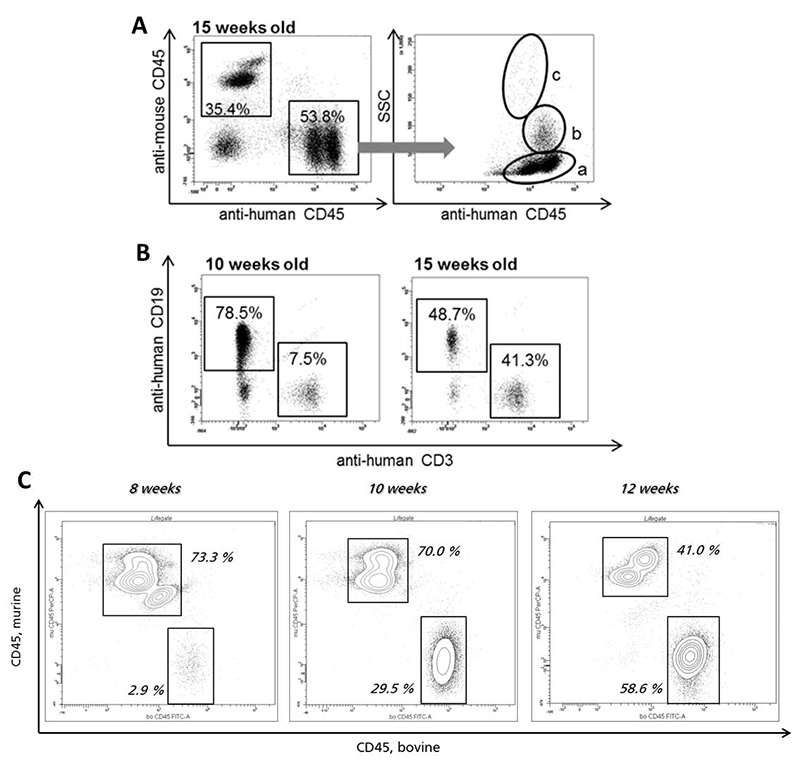
For the engraftment of xenogeneic immune systems the NSG mouse is currently the gold standard host because of its high grade immunodeficiency. In our group hematopoietic stem cells from different species and sources (e.g. cord blood, bone marrow) are used for this purpose. Newborn mice become preconditioned and afterwards transplanted with these cells. Within some weeks after transplantation, all main immune cell subpopulations develop in the NSG mice and constitute a functional xenogeneic immune system. After 8 to 10 weeks the xenogeneic, differentiated immune cells can be detected and quantified by flow cytometric analysis.
This model perfectly fits the demands of infection studies, the study of autoimmune and tumor diseases, and inflammatory research for the graft species.
- Pharmacodynamics and pharmacokinetics
- (Patho)physiological processes
- Therapeutic efficacy
- Proof of concept
Endpoints / outcome parameter
- Immune cells in full blood (in vivo)
- Cytokines, antibodies and protein levels (all murine and graft species) in blood plasma (in vivo)
- Histology of divers organs (ex vivo)
Readout parameter
- Flow cytometry
- ELISA / CBA (cytometric bead array)
- RT-PCR
- Western Blot
- Histology (various classical histological stains)
- Immunohistochemistry
Quality management and validation
- Controls
- Blinded induction
- Blinded data collection and analysis
- Randomisation
- Allocation concealment
- Biometric Expertise
- Internal quality management
References
Scholbach J, Schulz A, Westphal F, Egger D, Wege AK, Patties I, Köberle M, Sack U, Lange F. Comparison of hematopoietic stem cells derived from fresh and cryopreserved whole cord blood in the generation of humanized mice. PLoS One. 2012; 7(10):e46772.