Species
Mouse
Fields of application
Acute allergic asthma is induced by repeated intranasal administration of a whole dust mite extract. Besides impairment of lung function and distinct airway remodelling a number of immunological changes can be monitored for up to thirty days.
The model can be used for the following fields of application:
- Pharmacodynamics and pharmacokinetics
- (Patho)physiological processes
- Therapeutic efficacy
- Proof of concept
Endpoints / outcome parameter
- Dynamic compliance, Lung resistance, Enhanced pause (lung function measurement; in vivo)
- Immune cells in full blood (in vivo)
- IgE titre and cytokine levels in blood plasma (in vivo)
- Airway remodelling (upper airways and lung, including goblet cell hyperplasia, infiltration of eosinophils, fibrosis, airway narrowing; ex vivo)
- BALF (bronchoalveolar lavage fluid) immune cell composition, cytokine levels, IgE titre (ex vivo)
Readout parameter
- Invasive / non-invasive lung function measurements
- Flow cytometry
- ELISA / CBA (cytometric bead array)
- RT-PCR
- Western Blot
- Histology / Cytology (various classical histological stains)
- Immunohistochemistry
Quality management and validation
- Controls
- Blinded induction
- Blinded data collection and analysis
- Randomisation
- Allocation concealment
- Biometric Expertise
- Internal quality management
References
Cooperation project with Nuvo Research GmbH (Leipzig): "Die Entwicklung des Wirkstoffes WF10 zu einer innovativen Arzneimittel-Plattform zur Therapie chronisch inflammatorischer Erkrankungen"
Flemmig J, Schwarz P, Bäcker I, Leichsenring A, Lange F, Arnhold J. Rapid and reliable determination of the halogenating peroxidase activity in blood samples. J Immunol Methods. 2014; 415:46-56
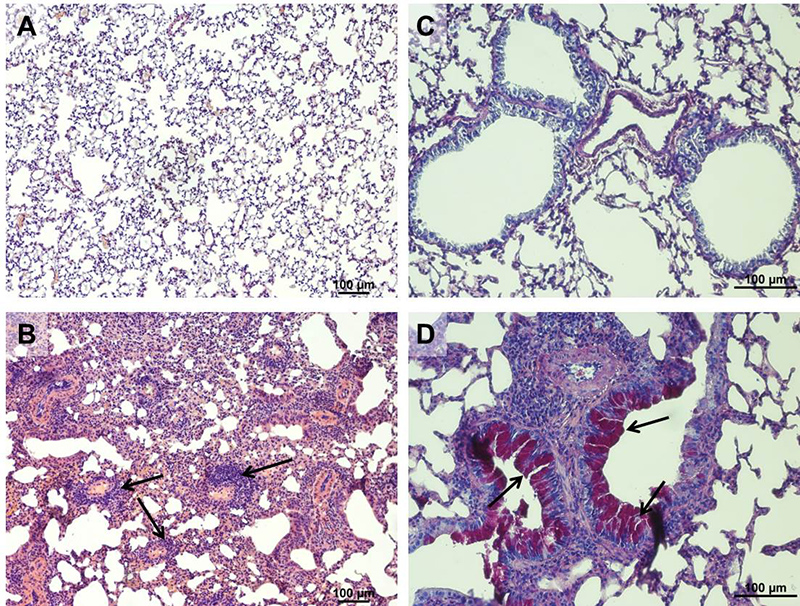
Airway remodelling in acute HDM induced allergic asthma in mice. A: Healthy lung tissue (HE stain). B: Fibrotic lung tissue of an allergic mouse. Besides fibrosis infiltration of eosinophils is clearly visible (arrows). C: Healthy lung tissue (PAS stain). D: Goblet cell hyperplasia and airway narrowing (arrows) in the lung of a mouse with acute HDM induced allergic asthma.