Species
mouse
Fields of application
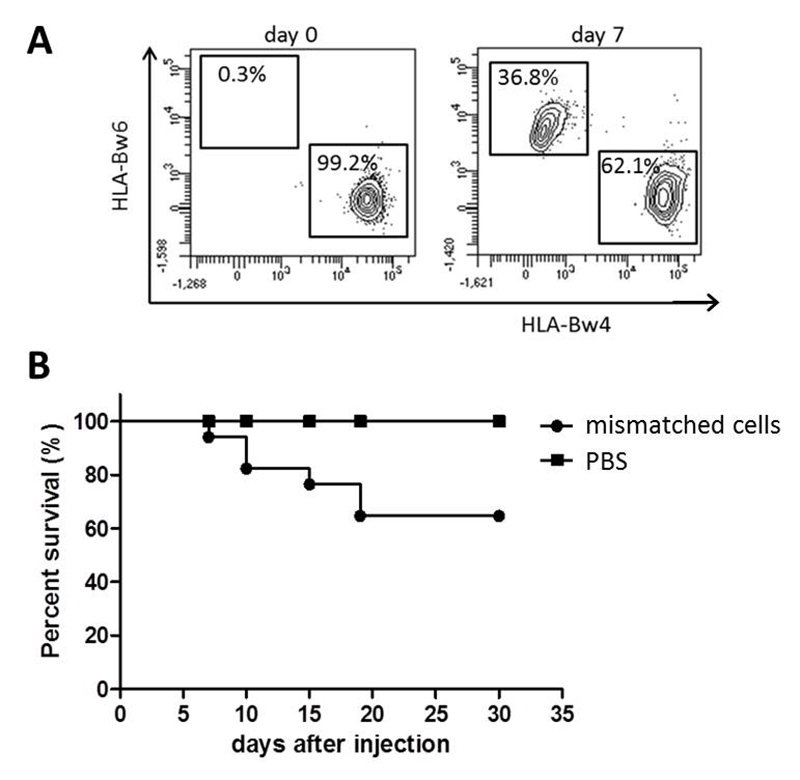
Stem cell transplantation is a necessary tool to treat hematological malignancies in patients but there are several unwanted side effects that can occur. Graft versus Host Disease (GvHD) is mainly caused by T cells from the donor that attack recipient cells. There are many mouse models that reflect GvHD on an interspecies level. To study reactions of human immune cells in vivo we use highly immunodeficient NSG mice transplanted with human CD34+ stem cells to engraft a functional human immune system. These humanized mice are preconditioned and receive a second transplantation with mismatched human immune cells and develop a human/human GvHD.
- Pharmacodynamics and pharmacokinetics
- (Patho)physiological processes
- Therapeutic efficacy
- Proof of concept
Endpoints / outcome parameter
- Score (severity of clinical symptoms; in vivo)
- Immune cells in full blood (in vivo)
- Cytokines, antibodies and protein levels (all human and murine) in blood plasma (in vivo)
- Cellular infiltrates in divers organs (ex vivo)
Readout parameter
- Scoring
- Flow cytometry
- ELISA / CBA (cytometric bead array)
- RT-PCR
- Western Blot
- Histology (various classical histological stains)
- Immunohistochemistry
Quality management and validation
- Controls
- Blinded induction
- Blinded data collection and analysis
- Randomisation
- Allocation concealment
- Biometric Expertise
- Internal quality management
References
Scholbach J, Schulz A, Westphal F, Egger D, Wege AK, Patties I, Köberle M, Sack U, Lange F. Comparison of hematopoietic stem cells derived from fresh and cryopreserved whole cord blood in the generation of humanized mice. PLoS One. 2012; 7(10):e46772.