Species
Mouse
Fields of application
The cartilage destruction model is used to investigate pathophysiological processes in the knee joint as seen in rheumatoid arthritis or other cartilage degenerative diseases. The cartilage destruction is induced by the transplantation of murine invasive fibroblasts into the knee joint of Balb/c mice. The resulting destruction is characterized by cell invasion into the cartilage and formation of a pannus. This model gives the opportunity to analyse processes leading to cartilage destruction in an immune competent animal. The potential of possible treatment options can be assessed.
- Pharmacodynamics and pharmacokinetics
- (Patho)physiological processes
- Therapeutic efficacy
- Proof of concept
Endpoints / outcome parameter
- Joint thickness (in vivo)
- Immune cells in full blood (in vivo)
- Cytokines and other protein levels in blood plasma (in vivo)
- Swelling, destruction, pannus formation, immune cell infiltration (ex vivo)
Readout parameter
- Measurement by means of a caliper
- Flow cytometry
- ELISA / CBA (cytometric bead array)
- RT-PCR
- Western Blot
- Histology (various classical histological stains)
Quality management and validation
- Controls
- Blinded induction
- Blinded data collection and analysis
- Randomisation
- Allocation concealment
- Biometric Expertise
- Internal quality management
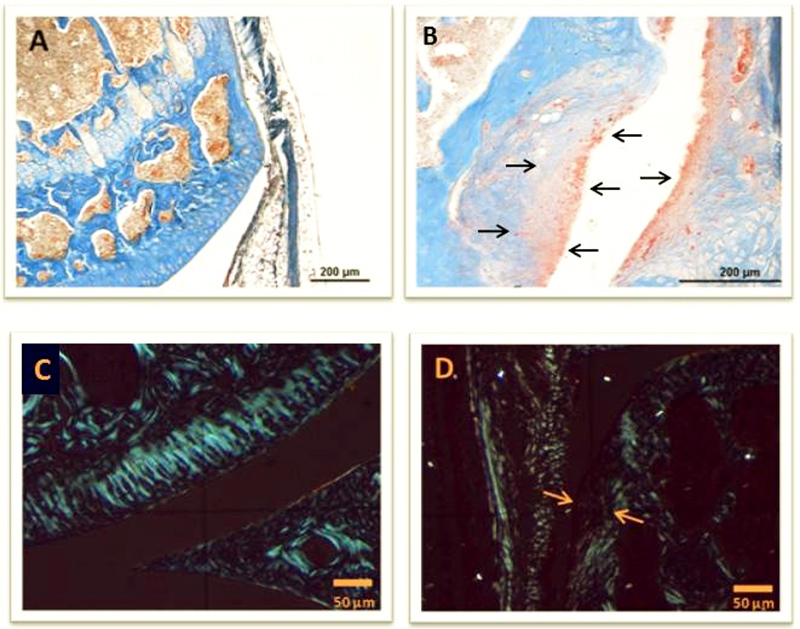
Histological changes in knee joints of Balb/c mice after transplantation of invasive fibroblasts. A: Healthy joint of a Balb/c mouse. KAO stained. B: Signs of destruction in a knee joint of a Balb/c mouse 4 weeks after transplantation of fibroblasts. KAO stained. C: Healthy joint of a Balb/c mouse in polarization microscope. D: Signs of destruction in a knee joint of a Balb/c mouse 4 weeks after transplantation of fibroblasts seen by polarization microscopy.